3:06 AM | 1
komentar | Read More
What is dengue fever? What is dengue hemorrhagic fever?
- Dengue [DEN-ghee] is a flu-like viral disease spread by the bite of infected mosquitoes. Dengue hemorrhagic fever is a severe, often fatal, complication of dengue.
- Dengue occurs in most tropical areas of the world. Most U.S. cases occur in travelers returning from abroad, but the dengue risk is increasing for persons living along the Texas-Mexico border and in other parts of the southern United States.
- There is no specific treatment for dengue.
- Prevention centers on avoiding mosquito bites in areas where dengue occurs or might occur and eliminating breeding sites.
What is dengue fever? What is dengue hemorrhagic fever?
Dengue fever is a flu-like illness spread by the bite of an infected mosquito.
Dengue hemorrhagic fever is a severe, often fatal, complication of dengue fever.
What is the infectious agent that causes dengue?
Dengue and dengue hemorrhagic fever are caused by any of the dengue family of viruses. Infection with one virus does not protect a person against infection with another.
How is dengue spread?
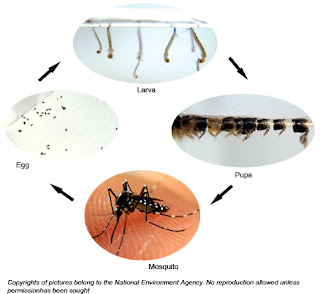
Dengue is spread by the bite of an Aedes mosquito. The mosquito transmits the disease by biting an infected person and then biting someone else.
Where is dengue found?
Dengue viruses occur in most tropical areas of the world. Dengue is common in Africa, Asia, the Pacific, Australia, and the Americas. It is widespread in the Caribbean basin. Dengue is most common in cities but can be found in rural areas. It is rarely found in mountainous areas above 4,000 feet.
The mosquitoes that transmit dengue live among humans and breed in discarded tires, flower pots, old oil drums, and water storage containers close to human dwellings. Unlike the mosquitoes that cause malaria, dengue mosquitoes bite during the day.
What are the signs and symptoms of dengue fever and dengue hemorrhagic fever?
Dengue fever usually starts suddenly with a high fever, rash, severe headache, pain behind the eyes, and muscle and joint pain. The severity of the joint pain has given dengue the name "breakbone fever." Nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite are common. A rash usually appears 3 to 4 days after the start of the fever. The illness can last up to 10 days, but complete recovery can take as long as a month. Older children and adults are usually sicker than young children.
Most dengue infections result in relatively mild illness, but some can progress to dengue hemorrhagic fever. With dengue hemorrhagic fever, the blood vessels start to leak and cause bleeding from the nose, mouth, and gums. Bruising can be a sign of bleeding inside the body. Without prompt treatment, the blood vessels can collapse, causing shock (dengue shock syndrome). Dengue hemorrhagic fever is fatal in about 5 percent of cases, mostly among children and young adults.
How soon after exposure do symptoms appear?
The time between the bite of a mosquito carrying dengue virus and the start of symptoms averages 4 to 6 days, with a range of 3 to 14 days. An infected person cannot spread the infection to other persons but can be a source of dengue virus for mosquitoes for about 6 days.
How is dengue diagnosed?
Dengue is diagnosed by a blood test.
Who is at risk for dengue?
Anyone who is bitten by an infected mosquito can get dengue fever. Risk factors for dengue hemorrhagic fever include a person's age and immune status, as well as the type of infecting virus. Persons who were previously infected with one or more types of dengue virus are thought to be at greater risk for developing dengue hemorrhagic fever if infected again.
What is the treatment for dengue and dengue hemorrhagic fever?
There is no specific treatment for dengue. Persons with dengue fever should rest and drink plenty of fluids. They should be kept away from mosquitoes for the protection of others. Dengue hemorrhagic fever is treated by replacing lost fluids. Some patients need transfusions to control bleeding.
How common is dengue?
In tropical countries around the world, dengue is one of the most common viral diseases spread to humans by mosquitoes. Tens of millions of cases of dengue fever and up to hundreds of thousands of cases of dengue hemorrhagic fever occur each year.
In the United States, approximately 100 cases of dengue are reported each year in travelers returning from tropical areas. Many more cases probably go unreported. A few persons have become infected with dengue while living in the United States. Aedes mosquitoes are found in Texas, Florida, and other southern states, and locally acquired dengue has been reported three times since 1980 in southern Texas.
Is dengue an emerging infectious disease?
Yes. All types of dengue virus are re-emerging worldwide and causing larger and more frequent epidemics, especially in cities in the tropics. The emergence of dengue as a major public health problem has been most dramatic in the western hemisphere. Dengue fever has reached epidemic levels in Central America and is threatening the United States.
Several factors are contributing to the resurgence of dengue fever:
- No effective mosquito control efforts are underway in most countries with dengue.
- Public health systems to detect and control epidemics are deteriorating around the world.
- Rapid growth of cities in tropical countries has led to overcrowding, urban decay, and substandard sanitation, allowing more mosquitoes to live closer to more people.
- The increase in non-biodegradable plastic packaging and discarded tires is creating new breeding sites for mosquitoes.
- Increased jet air travel is helping people infected with dengue viruses to move easily from city to city.
How can dengue be prevented?
There is no vaccine to prevent dengue. Prevention centers on avoiding mosquito bites when traveling to areas where dengue occurs and when in U.S. areas, especially along the Texas-Mexico border, where dengue might occur. Eliminating mosquito breeding sites in these areas is another key prevention measure.
Avoid mosquito bites when traveling in tropical areas:
- Use mosquito repellents on skin and clothing.
- When outdoors during times that mosquitoes are biting, wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants tucked into socks.
- Avoid heavily populated residential areas.
- When indoors, stay in air-conditioned or screened areas. Use bednets if sleeping areas are not screened or air-conditioned.
- If you have symptoms of dengue, report your travel history to your doctor.
- Eliminate mosquito breeding sites around homes. Discard items that can collect rain or run-off water, especially old tires.
- Regularly change the water in outdoor bird baths and pet and animal water containers.
3:05 AM | 0
komentar | Read More
Dengue attacked the Solok, One Dies
Written By Luthfie fadhillah on Sunday, March 13, 2011 | 7:58 AM
Disease dengue fever was spreading in Solok, West Sumatra. In the past two weeks, 18 people treated in hospitals Solok, and one person died., two people are still treated in this hospital.
"The number of patients within two weeks is quite a lot. Usually, patients with dengue fever are only 1-2 people," said Director of Solok Yusneli hospitals.
Patients with dengue fever from Solok City, Solok District, and surrounding areas. This condition has been reported to the local health department to obtain follow-up.
"The number of patients within two weeks is quite a lot. Usually, patients with dengue fever are only 1-2 people," said Director of Solok Yusneli hospitals.
Patients with dengue fever from Solok City, Solok District, and surrounding areas. This condition has been reported to the local health department to obtain follow-up.
7:58 AM | 0
komentar | Read More
Endemic area "Dengue Fever" in Sukabumi Spreads
Aegepty aedes mosquito attack in the city of Sukabumi, West Java, the more raged. Endemic spread of the disease dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) is increasingly widespread, even almost 95 percent of the area in Sukabumi dengue endemic area.
From the Health Office (DHO), Sukabumi, on Thursday, say, from 33 villages in the town of Sukabumi, as many as 31 villages of which is an endemic area of DHF. Two villages that are still safe from the spread of dengue is in Situ Blooming Village District and Village Overtime Situ Babakan Cibeureum District.
Head of Disease Control and Environmental Health (P2PL), Sukabumi City Health Office, Dr. Rita Fitrianingsih, said the current dengue endemic area increasingly widespread.
"Of the 27 villages that have been endemic area, now amount to 31 sub-district dengue endemic area," he said, saying the determination endemic areas due to frequent cases of dengue in 31 subdistricts.
According to Rita, the high cases of DHF are three factors which influenced the population density, hygienic behavior, and environmental hygiene.
"Public awareness of the need for environmental sanitation is still low, so many dengue cases. The movement to eradicate mosquitoes nest (PSN) should be encouraged back for handling the problem of DHF is a shared responsibility," said Rita.
According to him, until mid-January 2009, cases of dengue in the city of Sukabumi reached 100 cases and will likely have increased compared to cases of dengue fever in January 2008 that only as many as 123 cases.
He said, to suppress dengue cases in the city of Sukabumi company would like to fogging (fumigation) mass in a number of locations in the city of Sukabumi and PSN movement to the public.
From the Health Office (DHO), Sukabumi, on Thursday, say, from 33 villages in the town of Sukabumi, as many as 31 villages of which is an endemic area of DHF. Two villages that are still safe from the spread of dengue is in Situ Blooming Village District and Village Overtime Situ Babakan Cibeureum District.
Head of Disease Control and Environmental Health (P2PL), Sukabumi City Health Office, Dr. Rita Fitrianingsih, said the current dengue endemic area increasingly widespread.
"Of the 27 villages that have been endemic area, now amount to 31 sub-district dengue endemic area," he said, saying the determination endemic areas due to frequent cases of dengue in 31 subdistricts.
According to Rita, the high cases of DHF are three factors which influenced the population density, hygienic behavior, and environmental hygiene.
"Public awareness of the need for environmental sanitation is still low, so many dengue cases. The movement to eradicate mosquitoes nest (PSN) should be encouraged back for handling the problem of DHF is a shared responsibility," said Rita.
According to him, until mid-January 2009, cases of dengue in the city of Sukabumi reached 100 cases and will likely have increased compared to cases of dengue fever in January 2008 that only as many as 123 cases.
He said, to suppress dengue cases in the city of Sukabumi company would like to fogging (fumigation) mass in a number of locations in the city of Sukabumi and PSN movement to the public.
7:56 AM | 0
komentar | Read More
DHF patients in Bangkalan Rising
Patients with dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) in the Regional Hospital (RSD) Bangkalan, Madura, East Java, is constantly increasing.
According to Director of RSD Bangkalan Dr. Pradeep Andang, in December 2008 and then the number of patients stricken with dengue fever and was treated in 63 patients with RSD Bangkalan. However, in January 2009 increased to 117 patients.
"It means there is an increase of 54 people in January 2009 compared to December 2008," said Andang Pradata, in Bangkalan, on Tuesday.
DHF patients are generally treated in the RSD Bangkalan toddlers and children. There are also adults. However, relatively few in number and percentage is very small.
"It's never any adults, but we found a person and has now recovered," he said.
According habits, an increase of DHF in accordance with previous years, it occurred between January and February to early March.
Although patients improved, according to Andang, can not be expressed as outbreaks (outbreaks) because sufferers are spread in various districts in the region of Bangkalan, not in a particular village or district.
"The outbreak could be declared, if occurring in a particular region, at a time," said Pradeep Andang.
According to Director of RSD Bangkalan Dr. Pradeep Andang, in December 2008 and then the number of patients stricken with dengue fever and was treated in 63 patients with RSD Bangkalan. However, in January 2009 increased to 117 patients.
"It means there is an increase of 54 people in January 2009 compared to December 2008," said Andang Pradata, in Bangkalan, on Tuesday.
DHF patients are generally treated in the RSD Bangkalan toddlers and children. There are also adults. However, relatively few in number and percentage is very small.
"It's never any adults, but we found a person and has now recovered," he said.
According habits, an increase of DHF in accordance with previous years, it occurred between January and February to early March.
Although patients improved, according to Andang, can not be expressed as outbreaks (outbreaks) because sufferers are spread in various districts in the region of Bangkalan, not in a particular village or district.
"The outbreak could be declared, if occurring in a particular region, at a time," said Pradeep Andang.
7:54 AM | 1
komentar | Read More
Climate Change, Predicted Difficult Cycle DBD
Head of Health Office of West Kalimantan Province dr. Dawn said, climate change resulted in cycles of five annual dengue hemorrhagic fever in the province into changing and unpredictable.
"Now the increase in dengue cases could no longer be predicted based on the cycles of events," said dr. Dawn, in Pontianak, on Tuesday.
He explains, based on the cycles of events, Kalbar experiencing outbreaks (outbreaks) of DHF in the past five years. Events of the previous outbreak occurred in 2002, 1805 cases and 30 deaths. As in 2006, there was 1811 cases and 29 deaths.
"In 2006 his case more than in 2002. However, the toll of death and a little more," said Dawn.
He asked people not to reduce the level of vigilance against the threat of dengue fever since February to March the weather was still rainy season in West Kalimantan. The condition is very possible mosquito breeding aedes aegypti or the dengue causing mosquito.
He also appealed to residents not carelessly throw garbage and keep the surrounding environment by closing the rain shelter. Aedes aegypti mosquitoes breed in clear water and calm.
Meanwhile, according to data from the Health Office of Pontianak, throughout 2008, as many as 16 dengue positive patients died of 236 cases. That number increased compared to 2007, a total of 121 cases with three deaths.
DHF cases are most commonly found at Kelurahan Bangkong River as much as 28 cases, 26 cases pickaxe River and one patient in whom died, Parit Tokaya 24 cases and 3 died, Sungai Jawi In 23 cases and 1 died, Bangka Belitung 23 cases and 1 death .
In addition, in Kelurahan Sungai Jawi Foreign found as many as 22 cases with 4 of them died, Sungai Jawi 20 cases, 17 cases Pal Lima, Malay Continental Army 14 cases and 2 died, Siantan Hulu 7 cases and 1 death, 5 cases and the Upper Cape one dies, the Malay Sea Continental 5 cases and 1 died, Mariana 5 cases.
Later, Central District 4 cases, 4 cases Sekip Army, Middle Siantan 3 cases, 2 cases in Bugis, Siantan Downstream 2 cases and 1 died, Lower Cape 1 case, and Major Parit 1 case.
"Now the increase in dengue cases could no longer be predicted based on the cycles of events," said dr. Dawn, in Pontianak, on Tuesday.
He explains, based on the cycles of events, Kalbar experiencing outbreaks (outbreaks) of DHF in the past five years. Events of the previous outbreak occurred in 2002, 1805 cases and 30 deaths. As in 2006, there was 1811 cases and 29 deaths.
"In 2006 his case more than in 2002. However, the toll of death and a little more," said Dawn.
He asked people not to reduce the level of vigilance against the threat of dengue fever since February to March the weather was still rainy season in West Kalimantan. The condition is very possible mosquito breeding aedes aegypti or the dengue causing mosquito.
He also appealed to residents not carelessly throw garbage and keep the surrounding environment by closing the rain shelter. Aedes aegypti mosquitoes breed in clear water and calm.
Meanwhile, according to data from the Health Office of Pontianak, throughout 2008, as many as 16 dengue positive patients died of 236 cases. That number increased compared to 2007, a total of 121 cases with three deaths.
DHF cases are most commonly found at Kelurahan Bangkong River as much as 28 cases, 26 cases pickaxe River and one patient in whom died, Parit Tokaya 24 cases and 3 died, Sungai Jawi In 23 cases and 1 died, Bangka Belitung 23 cases and 1 death .
In addition, in Kelurahan Sungai Jawi Foreign found as many as 22 cases with 4 of them died, Sungai Jawi 20 cases, 17 cases Pal Lima, Malay Continental Army 14 cases and 2 died, Siantan Hulu 7 cases and 1 death, 5 cases and the Upper Cape one dies, the Malay Sea Continental 5 cases and 1 died, Mariana 5 cases.
Later, Central District 4 cases, 4 cases Sekip Army, Middle Siantan 3 cases, 2 cases in Bugis, Siantan Downstream 2 cases and 1 died, Lower Cape 1 case, and Major Parit 1 case.
7:53 AM | 0
komentar | Read More
Free, Patient Care DHF in Jakarta
DKI Jakarta Province emerintah again eliminate the cost of hospital care for patients with dengue hemorrhagic fever. Penggratisan cost done if the patient was treated in the third grade, at 17 hospitals owned by government, military, and police.
Chief Medical Officer Dien Emawati Jakarta, Tuesday (3 / 2) in Central Jakarta, said, penggratisan care costs has been discussed since January and has now come back into force. Penggratisan done so that the number of patients who died of dengue fever can be suppressed.
Penggratisan DHF patient care costs was lifted in mid-2008 because the number of patients has fallen dramatically. Penggratisan this time the cost of care provided to patients hospitalized in the third grade, with or without card poor families.
From early 2009 until Monday (2 / 2), the number of dengue patients reached 2134 people in Jakarta and four of them died. Dien said the number of dengue patients this year is much smaller than the number of patients in the same period of 2008, which reached 3047 people.
Penggratisan cost of care, Dien said, also applied to the flood victims. Residents who are suffering from floods can be checked by a health clinic or hospital to 17.
Chief Medical Officer Dien Emawati Jakarta, Tuesday (3 / 2) in Central Jakarta, said, penggratisan care costs has been discussed since January and has now come back into force. Penggratisan done so that the number of patients who died of dengue fever can be suppressed.
Penggratisan DHF patient care costs was lifted in mid-2008 because the number of patients has fallen dramatically. Penggratisan this time the cost of care provided to patients hospitalized in the third grade, with or without card poor families.
From early 2009 until Monday (2 / 2), the number of dengue patients reached 2134 people in Jakarta and four of them died. Dien said the number of dengue patients this year is much smaller than the number of patients in the same period of 2008, which reached 3047 people.
Penggratisan cost of care, Dien said, also applied to the flood victims. Residents who are suffering from floods can be checked by a health clinic or hospital to 17.
7:52 AM | 0
komentar | Read More
Within a month, 61 residents attacked in Banyuwangi DBD
During January 2009, as many as 61 residents Banyuwangi regency, East Java, tested positive for dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF).
Head of Health Office of Disease Eradication Banyuwangi M Izzudin said Tuesday, when compared to a decline in January 2008. A total of 94 patients treated at hospitals due to dengue in January last year.
Status of DBD in Banyuwangi not yet classified outbreaks (outbreaks). "Not to outbreaks. However, tend to be epidemics of DHF," he said.
The patients with DHF, according Izzudin, most originating from sub Cluring, Rogojampi, and Kabat. However, from 24 subdistricts in Banyuwangi regency, there is nothing clear of dengue outbreaks.
DHF patients from sub-city decline. The previous year the city district including dengue endemic area.
Izzudin annunciate, cadres Interpreters Monitoring larva (Jumantik) in the district of the city work well. The residents also perform environmental hygiene activities every Friday to perform activities of 3M and Mosquito Eradication nest (PSN).
Rainy season from January to March is estimated at most affected patients being treated for dengue. The number of patients affected by dengue fever in May and July decreased. August and September, DHF patients who were treated progressively decreasing and DHF patients will increase by approximately October to January.
Meanwhile, Head of Childcare Room Blambangan Hospital, Banyuwangi, Lilik Susiati argued, as many as 20 children were treated as positive for dengue. Some pediatric patients treated for dengue, also partly affected by dengue fever and typhoid complications.
Head of Health Office of Disease Eradication Banyuwangi M Izzudin said Tuesday, when compared to a decline in January 2008. A total of 94 patients treated at hospitals due to dengue in January last year.
Status of DBD in Banyuwangi not yet classified outbreaks (outbreaks). "Not to outbreaks. However, tend to be epidemics of DHF," he said.
The patients with DHF, according Izzudin, most originating from sub Cluring, Rogojampi, and Kabat. However, from 24 subdistricts in Banyuwangi regency, there is nothing clear of dengue outbreaks.
DHF patients from sub-city decline. The previous year the city district including dengue endemic area.
Izzudin annunciate, cadres Interpreters Monitoring larva (Jumantik) in the district of the city work well. The residents also perform environmental hygiene activities every Friday to perform activities of 3M and Mosquito Eradication nest (PSN).
Rainy season from January to March is estimated at most affected patients being treated for dengue. The number of patients affected by dengue fever in May and July decreased. August and September, DHF patients who were treated progressively decreasing and DHF patients will increase by approximately October to January.
Meanwhile, Head of Childcare Room Blambangan Hospital, Banyuwangi, Lilik Susiati argued, as many as 20 children were treated as positive for dengue. Some pediatric patients treated for dengue, also partly affected by dengue fever and typhoid complications.
7:51 AM | 0
komentar | Read More
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)